Models
ECOSMO Models
ECOSMO II
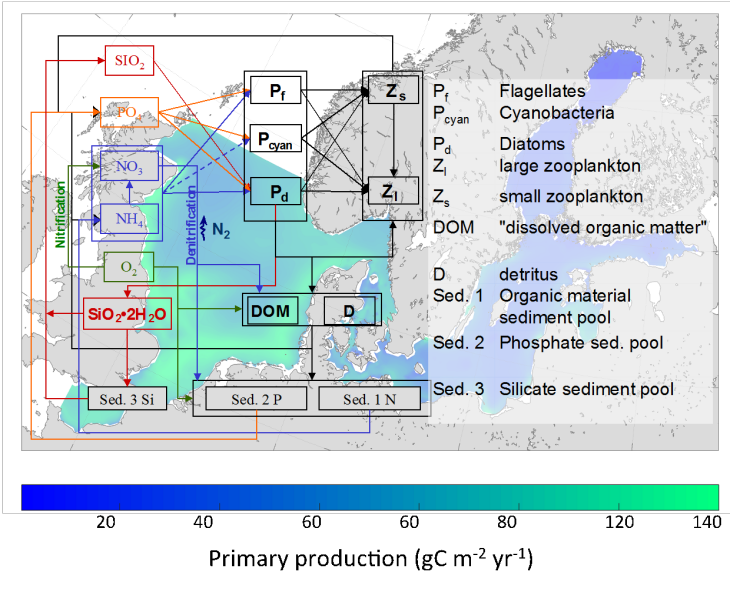
(Graphic: Ute Daewel/ Hereon)
ECOSMO II (ECOSystem Model) is a 3d fully coupled physical-biogeochemical model (Daewel and Schrum, 2013; Schrum et al., 2006a). The model is based on HAMSOM (HAMburg Shelf Ocean Model) North and Baltic Sea physics (Schrum, 1997; Schrum and Backhaus, 1999; Barthel et al. 2012). The biogeochemical processes in ECOSMO II are simulated using 16 state variables to resolve ecosystem dynamics by a functional group approach (Fig. 2). The model estimates two zooplankton functional groups, three phytoplankton groups, the nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon cycle, oxygen, detritus, biogenic opal, dissolve organic matter, and three sediment groups. The model was used for a multi-decadal long-term simulation and validated in detail (Daewel and Schrum, 2013, 2017a). The validated 3-d model data set is available through the coastDat database in daily resolution (Daewel & Schrum, 2017b), higher resolution upon request.
ECOSMO E2E
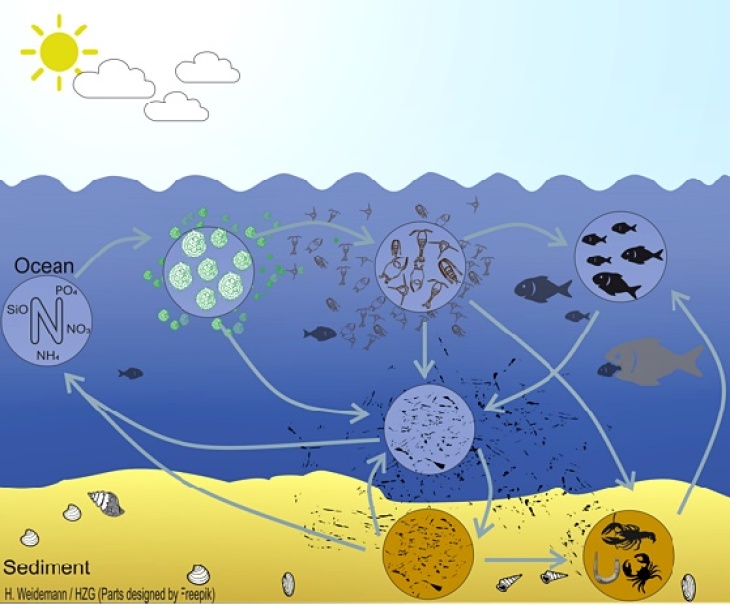
(Graphic: Hendrik Weidemann/ Hereon)
To address food web related questions in the Baltic Sea, we developed the 3d coupled ecosystem model ECOSMO E2E (Daewel et al. 2019), which is an NPZD-Fish modelling approach that bases on the ecosystem model ECOSMO II (Daewel and Schrum, 2013). The model represents both fish and macrobenthos as functional groups that are linked to the lower trophic levels via predator-prey relationships (Figure). The model allows investigating bottom-up impacts on primary and secondary production and cumulative fish biomass dynamics, but also bottom-up mechanisms on the lower trophic level production.
ECOSMO-CO2
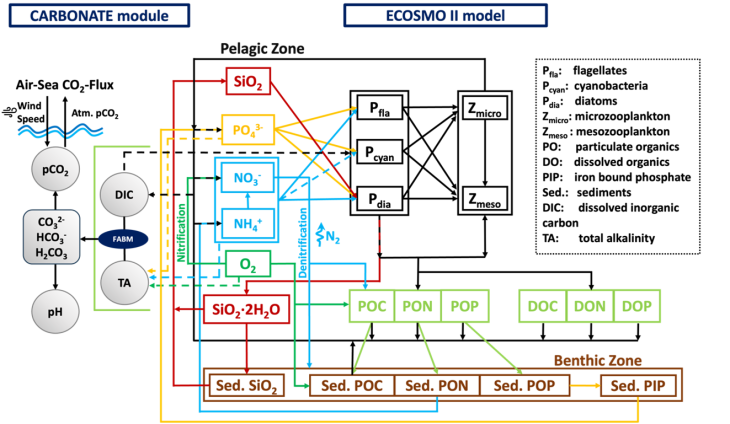
(Graphic: Kubilay Timur Demir/ Hereon)
ECOSMO II (ECOSystem Model) is a 3d fully coupled physical-biogeochemical model (Daewel and Schrum, 2013; Schrum et al., 2006a). The model is based on HAMSOM (HAMburg Shelf Ocean Model) North and Baltic Sea physics (Schrum, 1997; Schrum and Backhaus, 1999; Barthel et al. 2012). The biogeochemical processes in ECOSMO II are simulated using 16 state variables to resolve ecosystem dynamics by a functional group approach (Fig. 2). The model estimates two zooplankton functional groups, three phytoplankton groups, the nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon cycle, oxygen, detritus, biogenic opal, dissolve organic matter, and three sediment groups. The model was used for a multi-decadal long-term simulation and validated in detail (Daewel and Schrum, 2013, 2017a). The validated 3-d model data set is available through the coastDat database in daily resolution (Daewel & Schrum, 2017b), higher resolution upon request.
ECOSMO-ICE
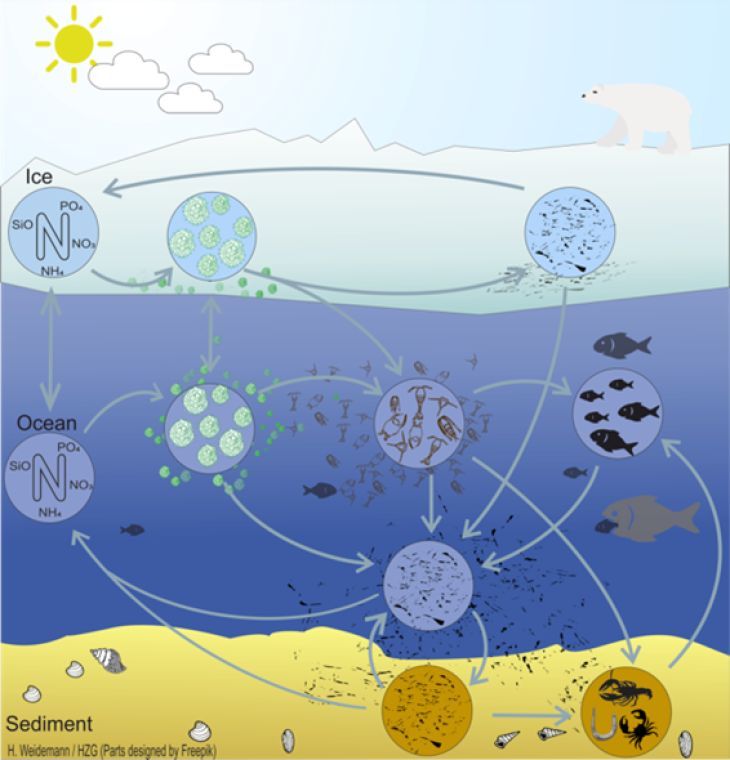
(Graphic: Hendrik Weidemann/ Hereon)
One of the most important characteristics of the Arctic ecosystem is the presence of a sea ice cover and the associated microbial communities, forming a sympagic ecosystem. To make ECOSMO E2E (Daewel et al., 2019) applicable to ice covered ecosystems, a sympagic system model was developed that allows online coupling to the existing model for the pelagic and benthic systems. Six state variables (sea-ice algae, four nutrient variables and one detritus group) were added to the original ECOSMO II model and exchange processes related to sea-ice formation and melting explicitely parameterized. An application in the Barents Sea shows that the sympagic system influences the timing and the amplitude of the pelagic primary and secondary production in the water column. (Benkort et al., 2020; Heath et al., 2022)
ECOSMO-IBM
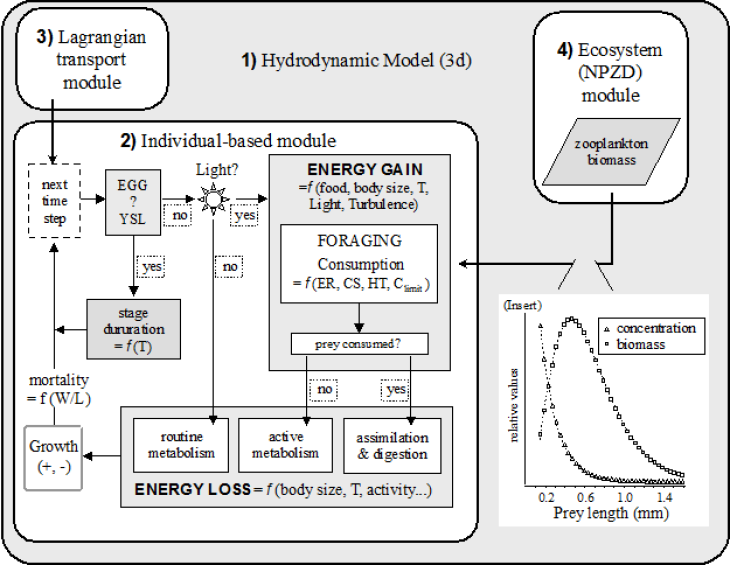
(Graphic: Ute Daewel/ Hereon)
Using spatially explicit Individual Based Models (ECOSMO-IBM) we are able to address scientific questions related to early life stages of marine species. With help of this model setup we can follow the trajectories of individual particles in both space and time. The ECOMSO-IBM model was first described by Daewel et al. (2008) in an application for sprat (Sprattus sprattus). An additional IBM submodule for North Sea Atlantic cod has been parameterized and described in detail by Daewel et al. (2011a). The latter has been used for a long-term simulation coupled to the ECOSMO II biogeochemistry to resolve changing potential of larvae survival in the North Sea (Daewel et al., 2015). A statistical IBM exists also for brown shrimp (Daewel et al., 2011b).
Further modules are available within the ECOSMO framework to resolve the fate and transport of pollutants (e.g. Bieser and Schrum, 2016, 2018 & Bieser et al. 2023). All ECOSMO modules are coupled using the framework for aquatic biogeochemical models FABM (Bruggeman and Bolding, 2014).
References
- Bruggeman, J., and Bolding, K. 2014. A general framework for aquatic biogeochemical models. Environmental Modelling and Software, 61: 249–265. Elsevier Ltd. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.04.002
- Blackford, J. C., & Gilbert, F. J. (2007). pH variability and CO2 induced acidification in the North Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 64(1-4), 229-241
- Barthel, K., Daewel, U., Pushpadas, D., Schrum, C.Årthun, M., & Wehde, H. (2012): Resolving frontal structures: On the computational costs and pay-off using a less diffusive but computational more expensive advection scheme. Ocean Dynamics, doi:10.1007/s10236-012-0578-9
- Benkort, D., Daewel, U., Heath, M., and Schrum, C. 2020. On the Role of Biogeochemical Coupling Between Sympagic and Pelagic Ecosystem Compartments for Primary and Secondary Production in the Barents Sea. https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fenvs.2020.548013
- Bieser, J., Amptmeijer, D.J., Daewel, U., Kuss, J., Soerensen, A.L., & Schrum, C. (2023): The 3D biogeochemical marine mercury cycling model MERCY v2.0 – linking atmospheric Hg to methylmercury in fish. Geosci. Model Dev., 16, 2649–2688, doi:10.5194/gmd-16-2649-2023
- Daewel, U., Peck, M.A., Kühn, W., St. John, M.A., Alekseeva, I., & Schrum, C. (2008): Coupling ecosystem and individual-based models to simulate the influence of environmental variability on potential growth and survival of larval sprat ( Sprattus sprattus L.) in the North Sea. Fish. Oceanogr. 17, 333–351, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2419.2008.00482.x
- Daewel, U., Peck, M.A.M.A., & Schrum, C. (2011): Life history strategy and impacts of environmental variability on early life stages of two marine fishes in the North Sea: an individual-based modelling approach. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 68, 426–443, doi:10.1139/F10-164
- Daewel, U., & Schrum, C.(2013): Simulating long-term dynamics of the coupled North Sea and Baltic Sea ecosystem with ECOSMO II: Model description and validation. Journal of Marine Systems 119, 30–49, doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.008
- Daewel, U., & Schrum, C. (2017): Low-frequency variability in North Sea and Baltic Sea identified through simulations with the 3-D coupled physical-biogeochemical model ECOSMO. Earth Syst. Dyn. 8, doi:10.5194/esd-8-801-2017
- Daewel, U., Schrum, C., and MacDonald, J. I. 2019. Towards end-to-end (E2E) modelling in a consistent NPZD-F modelling framework (ECOSMO E2E-v1.0): Application to the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Geoscientific Model Development, 12: 1765–1789
- Daewel, U., Schrum, C., & Gupta, A.K. (2015): The predictive potential of early life stage individual-based models (IBMs): an example for Atlantic cod Gadus morhua in the North Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 534, 199–219, doi:10.3354/meps11367
- Daewel, U., Schrum, C., & Temming, A. (2011): Towards a more complete understanding of the life cycle of brown shrimp (Crangon crangon): Modelling passive larvae and juvenile transport in combination with physically forced vertical juvenile migration. Fish. Oceanogr. 20, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2419.2011.00597.x
- Demir, K. T., Mathis, M., Kossack, J., Liu, F., Daewel, U., Stegert, C., Thomas, H., & Schrum, C. (2024). Variable organic matter stoichiometry enhances the biological drawdown of CO2 in the Northwest European shelf seas. EGUsphere, 2024, 1-47
- Heath, M. R., Benkort, D., Brierley, A. S., Daewel, U., Laverick, J. H., Proud, R., and Speirs, D. C. 2022. Ecosystem approach to harvesting in the Arctic: Walking the tightrope between exploitation and conservation in the Barents Sea. Ambio, 51: 456–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-021-01616-9
- Kossack, J., Mathis, M., Daewel, U., Liu, F., Demir, K. T., Thomas, H., & Schrum, C. (2024). Tidal impacts on air-sea CO2 exchange on the North-West European shelf. Frontiers in Marine Science, 11, 1406896
- Liu, F., Daewel, U., Kossack, J., Demir, K. T., Thomas, H., & Schrum, C. (2024). Evaluating ocean alkalinity enhancement as a carbon dioxide removal strategy in the North Sea. (Submitted to Biogeosciences)
- Peck, M.A., & Daewel, U. (2007): Physiologically based limits to food consumption, and individual-based modeling of foraging and growth of larval fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 347, 171–183, doi:10.3354/meps06976
- Schrum, C. (1997): A coupled ice-ocean model for the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Sensitivity of North Sea, Baltic Sea and Black Sea to anthropogenic and climatic changes. In: Özsoy, E., & Mukaelyan, A. (Eds.): Sensitivity of North Sea, Baltic Sea and Black Sea to Anthropogenic and Climatic Changes. Nato ASI Series. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp. 311–325.
- Schrum, C. (2001): Regionalization of climate change for the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Clim. Res. 18, 31–37.
- Schrum, C., Alekseeva, I., & St. John, M. (2006): Development of a coupled physical–biological ecosystem model ECOSMO. J. Mar. Syst. 61, 79–99, doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2006.01.005
- Schrum, C., & Backhaus, J.O. (1999): Sensitivity of atmosphere-ocean heat exchange and heat content in North Sea and Baltic Sea. A comparitive assessment. Tellus 51A. 526-549.
- Tiwari, P., Porz, L., Daewel, U., Kossack, J., Liu, F., Demir, K. T., Zhang, W., & Schrum, C.. Constraining Bottom Trawling Effects on North Sea Productivity: A Modeling Approach. (in preparation)
- Daewel, U., & Schrum, C. (2017): ECOSMO II hindcast simulations for the North Sea and Baltic Sea (1948-2008). World Data Center for Climate (WDCC) at DKRZ. doi:10.1594/WDCC/ECOSMOII_NCEP.1948-2008
- Samuelsen, A., Schrum, C., Castano Primo, R., Yumruktepe, C.V., & Daewel, U. (2018): A model hindcast of bottom environmental conditions in the North Atlantic Ocean 1948 to 2014. Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, PANGAEA, doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.889396
- Alekseeva, I., Jarsjö, J., Destouni, G., & Schrum, C. (2009): Reproducing the Aral Sea water budget and sea–groundwater dynamics between 1979 and 1993 using a coupled 3-D sea-ice– groundwater model. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.03.018
- Alekseeva, I., & Schrum, C. (2008): Historical reconstruction of the Aral Sea shrinking by a full 3-d wetting and drying model ECOSMO. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., 1, S92–S98
- Bieser, J., & Schrum, C. (2016): Impact of Marine Mercury Cycling on Coastal Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations in the North- and Baltic Sea region. Elementa, Science of the Anthropocene, 4:000111, doi:10.12952/journal.elementa.000111
- Bieser, J., & Schrum, C. (2018): Evaluation of the Impact of Air-Sea Exchange on Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations. In: Mensink C., & Kallos G. (eds): Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXV. ITM 2016. Springer Proceedings in Complexity. Springer, Cham, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-57645-9_69
- Burt, W.J., Thomas, H., Pätsch, J., Omar, A.M., Schrum, C., Daewel, U., Brenner, H., & Baar, de H.J.W. (2014): Radium isotopes as a tracer of sediment-water column exchange in the North Sea. Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 28, doi:10.1002/2014GB004825
- Chust, G., Allen, J.I., Bopp, L., Schrum, C., Holt, J., Tsiaras, K., Zavatarelli, M., Chifflet, M., Cannaby, H., Dadou, I., Daewel, U., Wakelin, S.L., Machu, E., Pushpadas, D., Butenschon, M., Artioli, Y., Petihakis, G., Smith, C., Garçon, V., Goubanova, K., Le Vu, B., Fach, B.A., Salihoglu, B., Clementi, E., & Irigoien, X. (2014): Biomass changes and trophic amplification of plankton in a warmer ocean. Glob. Chang. Biol. 20, 2124–39, doi:10.1111/gcb.12562
- Christensen, A., Daewel, U., Jensen, H., Mosegaard, H., St. John, M., & Schrum, C. (2007): Hydrodynamic backtracking of fish larvae by individual-based modelling. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 347, 221-232
- Christensen, A., Jensen, H., Mosegaard, H., St. John, M., & Schrum, C. (2008): Sandeel larval transport patterns in North Sea from an individual-based hydrodynamic egg and larval model. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 65-7, 1498-1511
- Daewel, U., Peck, M.A., Schrum, C., & St. John, M. (2008): How best to include the effects of climate-driven forcing on prey fields in larval fish individual based models. Journal of Plankton Research, 30, 1-5
- Harms, I., Schrum, C., & Hatten, K. (2005): Numerical sensitivity studies on the variability of climate relevant processes in the Barents Sea. JGR, J. Geophys. Res., 110, C06002, doi:10.1029/2004JC002559
- Holt, J., Schrum, C., Cannaby, H., Daewel, U., Allen, I., Artioli, Y., Bopp, L., Butenschon, M., Fach, B.A., Harle, J., Pushpadas, D., Salihoglu, B., & Wakelin, S. (2016): Potential impacts of climate change on the primary production of regional seas: A comparative analysis of five European seas. Prog. Oceanogr. 140, doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2015.11.004
- Holt, J., Schrum, C., Cannaby, H., Daewel, U., Allen, I., Artioli, Y., Bopp, L., Butenschon, M., Fach, B., Harle, J., Pushpadas, D., Salihoglu, B., & Wakelin, S. (2014): Physical processes mediating climate change impacts on regional sea ecosystems, Biogeosciences Discuss., 11, 1909-1975, www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/11/1909/2014/, doi:10.5194/bgd-11-1909-2014
- Hufnagl, M., Payne, M., Lacroix, G., Bolle, L.J., Daewel, U., Dickey-Collas, M., Gerkema, T., Huret, M., Janssen, F., Kreus, M., Pätsch, J., Pohlmann, T., Ruardij, P., Schrum, C., Skogen, M.D., Tiessen, M.C.H., Petitgas, P., Beek, van J.K.L., Veer, van der H.W., & Callies, U. (2017): Variation that can be expected when using particle tracking models in connectivity studies. J. Sea Res., doi:10.1016/j.seares.2017.04.009
- Jansen, T., Kristensen, K., Payne, M., Edwards, M., Schrum, C., & Pitois, S. (2012): Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Mackerel Spawning in the North Sea: A New Time Series and Modeling Approach to CPR Data. PLoSOne, Marine and Aquatic Sciences, 7, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038758
- Janssen, F., Schrum, C., Hübner, U., & Backhaus, J.O. (2001): Uncertainty analysis of a decadal simulation with a regional ocean model for the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Clim. Res. 18, 55–62
- Jarsjö, J., Alekseeva, I., Schrum, C., & Destouni, G. (2005): Simulation of groundwater - sea water interactions in the Aral Sea basin by a coupled water balance model. Calibration and Reliability in Groundwater Modelling: From Uncertainty to Decision Making (Proceedings of ModelCARE’2005, The Hague, The Netherlands, June 2005). IAHS Publ. 304, pp.261–267
- Maar, M., Butenschön, M., Daewel, U., Eggert, A., Fan, W., Hjøllo, S.S., Hufnagl, M., Huret, M., Ji, R., Lacroix, G., Peck, M.A., Radtke, H., Sailley, S., Sinerchia, M., Skogen, M.D., Travers-Trolet, M., Troost, T.A., & Wolfshaar, van de K. (2018): Responses of summer phytoplankton biomass to changes in top-down forcing: Insights from comparative modelling. Ecol. Modell. 376, 54–67, doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2018.03.003
- Pushpadas, D., Schrum, C., & Daewel, U. (2015): Projected climate change impacts on North Sea and Baltic Sea: CMIP3 and CMIP5 model based scenarios. Biogeoscience discussions, 12, 12229-12279, 2015 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/12/12229/2015/, doi:10.5194/bgd-12-12229-2015
- Rindorf, A., Jensen, H., & Schrum, C. (2008): Growth, temperature and density relationships of North Sea. Canadian Journal of Fisheries Res, 456-470
- Schrum, C., Siegismund, F., & St. John, M. (2003): Decadal Variations in the stratification and circulation patterns of the North Sea. Are the 90’s unusual? ICES Symposium of Hydrobiological Variability in the ICES area 1990-1999, ICES Journal of Marine Science, Symposia series, Vol. 219, 121-131
- Schrum, C., St. John, M., & Alekseeva, I. (2006): ECOSMO, a coupled ecosystem model of the North Sea and Baltic Sea: Part II. Spatial-seasonal characteristics in the North Sea as revealed by EOF analysis. Journal of Marine Systems, doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2006.01.004
- Schrum, C., Harms, I., & Hatten, K. (2005): Modelling Air-sea exchange in the Barents Sea By using a coupled regional ice-ocean model. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 14, No. 6, 1-3, doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2005/0075
- Skogen, M.D., Drinkwater, K., Hjøllo, S.S., & Schrum, C. (2011): North Sea sensitivity to atmospheric forcing. Journal of Marine Systems, doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.12.008
- Årthun, M., Bellerby, R.G.J., Omar, A.M., & Schrum, C. (2012): Air-sea CO2 fluxes in the Barents Sea as determined from empirical relationships. Journal of Marine Systems, doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.03.005
- Årthun, M., Ingvaldsen, R., Smedsrud, L.H., & Schrum, C. (2011): Dense Water formation and circulation in the Barents Sea. Deep Sea Research I 58, 801-817
- Årthun, M., & Schrum, C. (2010): Ocean surface heat flux variability in the Barents Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 83, 88-98
